WHAT IS “HUMAN LIFE” Part-9
When describing “The Human” we ought to know the physical and functional aspect first, without which the knowledge is incomplete. This blog is in continuation of past blog 8 in Brief.
F: Urinary system/Excretory System
This system includes series of organs starting from kidney to ureter ,bladder ending at urethra. Both kidneys are bean shaped, Right is placed behind the liver, Left is behind the stomach and spleen on both side of the vertebra extending from 12th thoracic up to 3rd lumbar below. urine is filtered out when blood passes through the kidney. It is responsible for maintaining fluid, electrolytes and acid-base balance of the body.

G: Endocrine system
It is responsible for the production of various hormones which regulate different body functions including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
H: Integumentary system
This is most visible exterior organ of the body includes skin, hair, nail and glands. Important functions are protection, regulation, sensation, production.
- Sweat gland : regulate the body temperature by producing and releasing sweat.
- Apocrine gland : the exact function of this gland yet unknown. It is suggested that it has some role in pheromone production in some animals including Human.
- Sebaceous gland : responsible for lubrication of skin and hair by secreting sebum. Sebum has got anti-microbial properties , also helps in preventing skin from uv radiation, heat and cold .
I: Reproductive system (Female and Male)
This system is collection of organs and tissues different in both sexes which work to facilitate sexual reproduction of Human and are inter dependent.
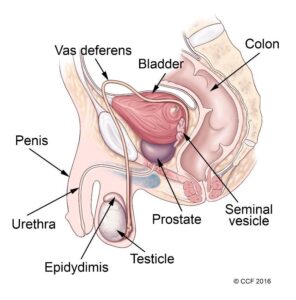
Male Reproductive system includes
- Testis -one each side of the scrotal pouch responsible for production of sperm and male sex hormone ,the testosterone
- Epididymis – situate on back of the testis ,long coil tube ,responsible for maturation of sperm.
- Vas deferens – tube for transport of sperm from epididymis to ejaculatory duct .
- Seminal vesicles – situated at the base of bladder secrets fluid that makes semen.
- Prostate gland -situated below the bladder at the neck ,secrets milky white fluid that nourish and protect the sperm.
- Bulbourethral gland – a pair of gland beneath the prostrate that secretes the fluid and lubricate the urethra.
- Urethra – the tube that runs through the penis and carries both semen and urine out of the body.
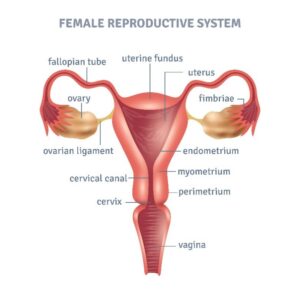
Female Reproductive system
- The system is one of the complex system of the human and vital for perpetuation of the human species. It has critical role during development of the fetus for diversity of the species. It includes a pair of fallopian tube single uterus, cervix and vagina.
- Ovaries – almond shaped organ on both sides of the uterus. It produces single egg during each ovulation time, responsible for production of female sex hormone mainly estrogen and progesterone.
- Fallopian tubes – a pair of tubes, one on each sides connected to ovary one end and uterus to the other end. Eggs are fertilised by sperms in the tube, which comes from vagina during intercourse. The fertilised eggs are carried to the uterus for the implantation .
- Uterus – it is called womb of the mother, where fertilised eggs(zygote) are implanted and develops into full grown fetus. The lining of the uterus sheds blood and other products during menstruation in each month if pregnancy doesn’t occur.
- Cervix – lower part of the uterus plays a vital role during labor and delivery of fetus.
- Vagina – It connects the cervix inside to the outside.
- It is a muscular channel through which menstrual blood comes out, also helps in birth of the baby. It is the organ of sexual intercourse.
- In addition to this structure female reproductive system also includes breasts meant for milk production and breast feeding.
Philosophically modern reproduction is drawn into controversy due to advancement of knowledge and technology in reproduction. There are argument and counter argument on reproductive autonomy, reproductive guide and reproductive choices. Moral values are analyzed now a days in carrying out other reproductive procedures like in-vitro fertilization and surrogacy.
J: Immune system
Immune system is very much complex, integrated ,coordinated structures comprising cells ,tissues ,organs and proteins. Primary lymphoid organ are thymus and bone-marrow. Secondary organs are spleen, tonsil, lymph vessel, lymph node, adenoids, skin and liver. It works for defending or limiting infections invaded by bacteria, virus, parasites, toxins, fungi and cancerous cells .
- Adaptive/Acquired Immunity – Day one after birth the baby-body is exposed to outer environment and comes in contact with various pathogens and immunity is produced against each. The body keeps a record copy. When re-exposures happens the body deal with invaders quickly.
- Innate Immunity – It is the first line of defence against pathogens. It includes skin and mucous membrane of throat and gout. The response is general and non specific.
- Passive Immunity – it is temporary type of immunity derived from another person. Through placenta during pregnancy and through breast milk during breast feeding ,the antibodies from mother comes to the baby .
WHO has put much stress on maternal and child health in order to make a healthy wellbeing and above all healthy society.
Sometime however immune system may go wrong ,mistakenly attack the body’s own cell and destroy it. This is called autoimmune disorder Some times pathogens are able to suppress or evade the immune system leading to chronic infection. Disease and disorder of health are under constant and progressive research so as to prolong the life and maintain good health. In this respect WHO has come out with definition of good health.